Seed funding rounds are typically small and are channeled toward research and development of an initial product. The money may also be used for conducting market research or expanding the team. There are seed accelerators out there, that accept applicants, provide seed capital and offer an opportunity to demo a solution to major investors.
1. 4 - 10+ years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs are developing and polishing business & operations plan.
3. Founding entrepreneurs develop the business model, company goals and long-term
product strategy.
4. VC provides startup capital and helps refine the planning process.
Stage 2: Startup capital
This stage is similar to the seed stage. With initial market analysis conducted and business plans in place, companies look to begin marketing and advertising the product and acquiring customers.
Organizations at this stage likely have at least a sample product available. VC funding may be diverted to acquiring more management personnel, fine-tuning the product/service or conducting additional research.
1. 3 - 8+ years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs are developing and polishing business & operations plan.
3. Founding entrepreneurs develop the business model, company goals and long-term
product strategy.
4. VC provides startup capital and helps refine the planning process.
Stage 3: Early stage/first stage/second stage capital
Though sometimes called “first stage,” this stage only comes after the seed and startup ones in most cases. Funding received at this stage will often go toward manufacturing and production facilities, sales and more marketing.
The amount invested here may be significantly higher than during prior stages. At this point, the company may also be moving toward profitability as it pushes its products and advertisements to a wider audience.
1. 3 - 7 years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs focus on working on product development.
3. Key managers and technical experts develop product prototypes.
4. VC funds and supports operating and development efforts.
Stage 4: Expansion stage/second stage/third stage capital
Growth is often exponential by this stage. Accordingly, VC funding serves as more fuel for the fire, enabling expansion to additional markets (e.g., other cities or countries) and diversification and differentiation of product lines.
With a commercially available product, a startup at this stage should be taking in ample revenue, if not profit. Many companies that get expansion funding have been in business for two to three years.
“VC funding serves as more fuel for the fire, enabling expansion to additional markets and diversification and differentiation of product lines.”
Initial Expansion Stage
1. 2 - 5 years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs focus on product refinement.
3. Company tests, refines and starts initial manufacturing of prototypes to eliminate major
technical or product risks.
4. VC finances operations and provides business expansion expertise.
Secondary Expansion Stage
1. 1 - 4 years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs focus on scaling marketing efforts.
3. Management works to increase market presence and develop second generation products.
4. VC provides funding and consultation to achieve positive cash flow.
Stage 5: Later Stage/Mezzanine/bridge/pre-public stage
After reaching this juncture, the company may be looking to go public, given that its products and services have found suitable traction. Funds received here can be used for activities such as:
If all goes well, investors may sell their shares and end their engagement with the company, having made a healthy return. Many tech IPOs – think Facebook, Twitter and Yelp – were only possible after years of VC funding that fueled user and revenue growth. There’s a saying that there’s no such thing as a free lunch, and VC funding of free apps and services is a good case in point.
1. 0 - 2 years to exit.
2. Founding entrepreneurs focus on profitablity.
3. VC and management team position the company for an IPO or acquisition. IPO/Acquisition
- Entrepreneurs, management, employees and VCs are rewarded for hard work and
investment - cash-out subject to lock-up period and SEC restrictions.
So you can use pgf500 platform, open your own project, and enter all your info in the Sustainable Business Model Canvas.
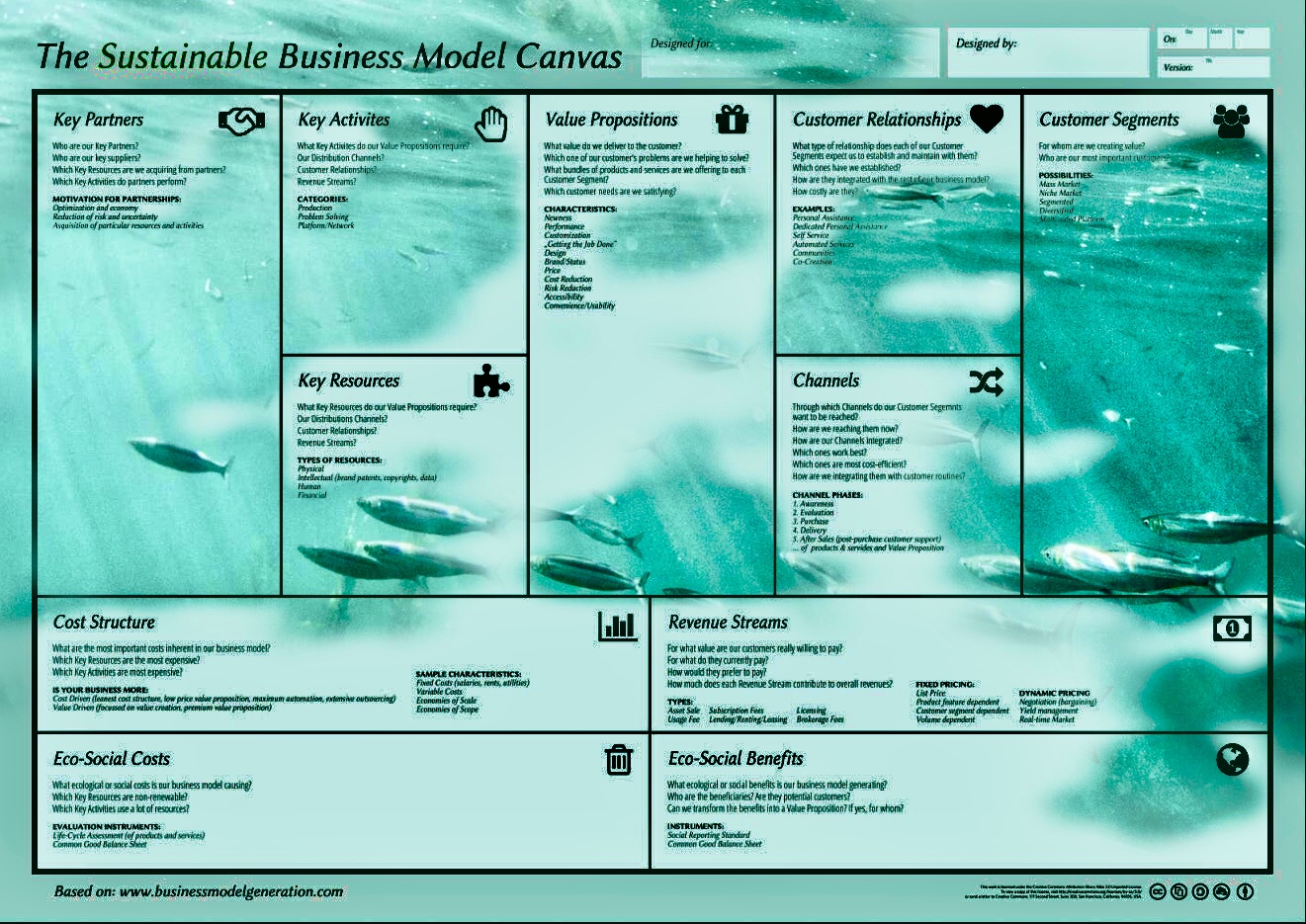
Once this is done, since you have 15 days of free trial, you can create a pivot of your project and invite your team to the second project, simply by entering their emails in “Team”.
At this point you and your team can work on the new strategy, a new business model, experimenting with new actions and seizing new opportunities.
Remember that all the information in the 11 fields of the Sustainable Business Model Canvas is important.
In addition, you can also turn your business green, in order to become sustainable and carbon-neutral, Net Zero.

If you want to better understand what a business model is, find some insights at these links:
Business Model Canvas
